A sudden increase in Black Fungus cases has been recorded from several parts of India during the second wave of COVID-19. Meanwhile, cases of White Fungus, which is considered more dangerous than Black Fungus.
What is Black Fungus?

source: usatoday.com
Mucormycosis is the medical term for black fungus. It is an unusual fungal infection caused by environmental exposure to mucor mold. It is catchable if the fungus “enters the skin through a cut, burn, or other types of skin trauma.”
Symptoms
- Headache
- Facial pain
- Nasal congestion
- Loss of vision or pain in the eyes
- Swelling in cheeks and eyes
- Black crusts in the nose
Treatment
source: dnaindia.com
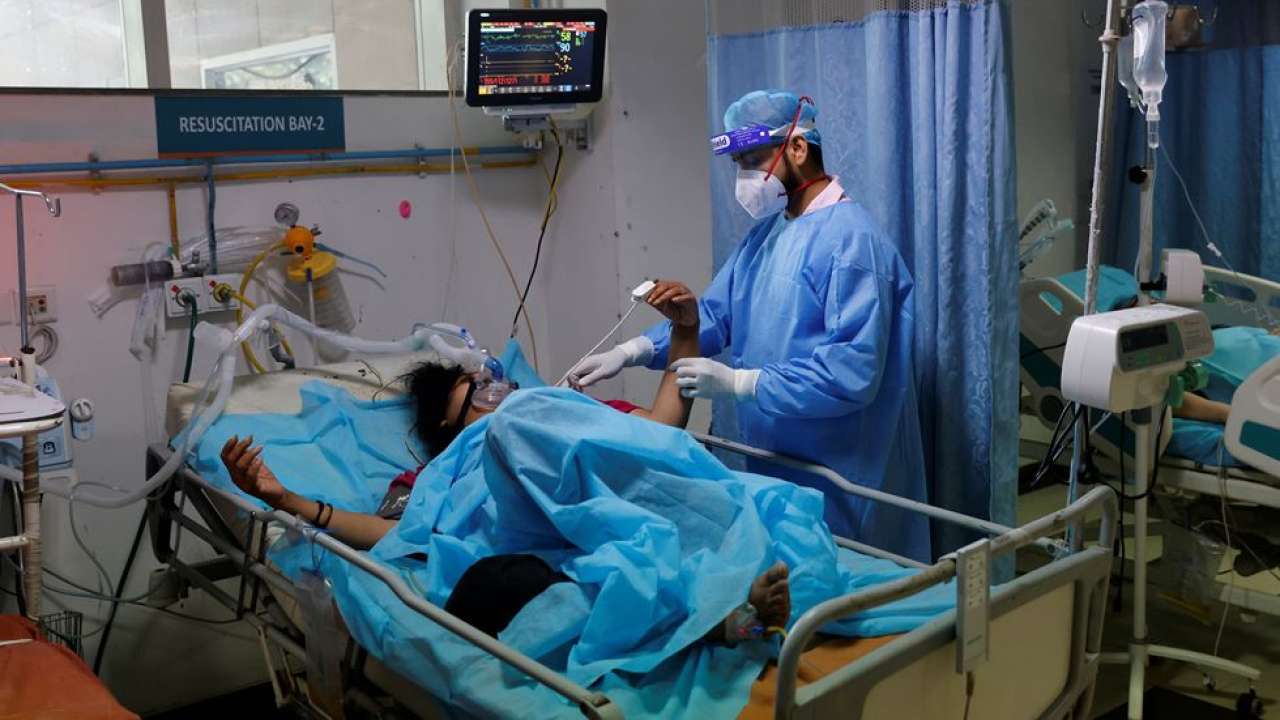
After infecting a human, the Black Fungus spreads through the nose, attacks the eyes, and then enters the brain. If the infection spreads to the brain, treating the patient becomes difficult, and the patient’s chances of survival are low. Both infected tissues must be surgically removed. Some patients lose one or both eyes, as well as the upper lip in some cases. It is important to use steroids wisely in consultation with a doctor and to keep blood sugar levels under control. Patients can need an intravenous antifungal injection that lasts four to six weeks.
In the meantime, the Centre has asked states to make it a notifiable disease. It is also working to resolve the scarcity of Amphotericin B, the medication used to treat the disease. Each infected person can need up to 20 vials of this injection, with each vial costing between Rs 5,000 and Rs 6,000.
What Is White Fungus?
source: weather.com
White Fungus is a fungal infection caused by the candida group of organisms that results in the formation of whitish membranes or discharge. Candidiasis is a fungal infection that causes white fungus. It may be caused by the use of infected oxygen cylinders or by the excessive use of steroids. It targets organs such as the lungs, skin, nails, brain, kidney, and mouth. Young children, like adults, are sensitive to White Fungus infection. If this fungus spreads across the body, it becomes more toxic. When it affects the lungs or blood, the chances of survival are lower than when it affects other areas of the body.
Symptoms
- Cough
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- White discharge
- White patches in oral cavity
- Chest pain, reduced oxygen level
- Dark spots on lungs
Note: The symptoms of ‘white fungus’ are similar to those of COVID-19 symptoms, and the infection can be detected using a CT scan or an X-ray.
Who is at a higher risk of infection with White Fungus?

source: sentinelassam.com
Both the White and Black fungus focus on people with weakened immune systems. In addition, people who have diabetes, cancer, a serious condition, or are in the intensive care unit are more vulnerable to black fungus. Simultaneously, the white fungus affects people who have chronic health conditions. People with high blood sugar level and cancer are more at risk to white fungus.
Treatment
Patients infected with White Fungus may be treated with antifungal medications. Candidiasis may be treated orally with fluconazole or itraconazole. Infections of the oral cavity or genitourinary regions will necessarily require topical applications. Caspofungin or micafungin are used to treat serious infections in critically ill patients. Furthermore, White Fungus can be avoided by properly sanitising ventilators/oxygen cylinders, as well as by taking good care of medical equipment used on patients.





